
One example is the chemical energy in food that we turn into kinetic energy when we move. This law states that energy is never created or destroyed, it is only changed from one state to another. There are other units of measure for energy that are used throughout the world including kilowatt-hours, calories, newton-meters, therms, and foot-pounds. In physics, the standard unit of measure for energy is the joule which is abbreviated as J. Another example is a book sitting high on a shelf. One example of this is a spring that is pressed all the way down.

It takes energy to cook food, to drive to school, and to jump in the air.Įnergy can take a number of different forms. It's everywhere around us and takes all sorts of forms. The microwave oven works with the concept of radiant energy (electromagnetic waves).The simplest definition of energy is "the ability to do work". For example, when micro-waves (which forms part of the entire spectrum) are set-off in a microwave oven, the water molecules in the food are charged and caused to vibrate billions of times per second, generating heat that causes the food to cook. When radiant energy comes into contact with matter, it changes the properties of that matter. In the illustration above, you will see the different radiant energy levels represented by their wavelengths. White light, for example, is a form of radiant energy, and its frequency forms a tiny bit of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. The shorter the wavelength, the higher its frequency, and vice versa. The entire wave system from the lowest frequency to the highest frequency is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. There are different kinds of electromagnetic waves, and all of them have different wavelengths, properties, frequencies, and power, and all interact with matter differently. The energy in the electromagnetic waves is what we call radiant energy. That is possible by electromagnetic waves. The sun’s heat is not transmitted through any solid medium but a vacuum. For example, we receive the heat from the sun, which is located very far from the earth via radiation. It is a form of energy that can travel through space.

These waves resemble the ripple (mechanical) waves you see when you drop a rock into a swimming pool, but with electromagnetic waves, you do not see them, but you often can see the effect of it. Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves. Now, the electrical field induced causes waves, called electromagnetic waves, and they can travel through a vacuum (air), particles or solids. That is possible by electromagnetic waves.īefore we go any further, let us understand what electromagnetic waves are.Įach time static energy from electric and magnetic force comes together, they induce an electric field around them.Īn example of an electric static force is the shock you get when you hold a metal doorknob.Īn example of a magnetic force is the pull that attracts metals to the magnet.

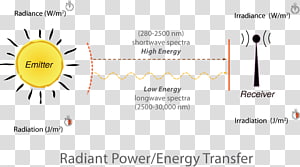
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
